What Is Corporate Social Responsibility?
Doing Well by Doing Good

© GettyImages
alvarez
CSR can help your company give back to the planet and its people, and improve profits.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is nothing new. But in recent years, CSR programs have changed from being a "nice to have" to an essential for many businesses.
Events such as the Volkswagen Emissions scandal of 2015, the 2008 subprime mortgage crisis and the collapse of Lehman Bros, and BP's Deepwater Horizon spill in 2010, along with rising concern about pollution and climate change, have spurred many organizations to take a deeper look at the social, ethical and environmental impact of their activities.
In this article, we'll learn more about the different types of CSR programs organizations use, the benefits they can provide to stakeholders, and how to develop a successful CSR strategy.
What Is Corporate Social Responsibility?
Corporate social responsibility (also known as corporate citizenship and responsible business) refers to the philanthropic, environmental or community-based activities undertaken by a company to create a positive social impact.
CSR is often seen as a form of self-regulation, which empowers organizations to operate in a socially responsible way and to go beyond what is required of them by law.
Many businesses engage in these kinds of programs for strategic or ethical purposes, but they have also been found to enhance brand reputation and increase profits.
Traditionally, CSR tends to cover three key areas – the environment, ethics and philanthropy:
1. Environmental Responsibility
This is one of the most common forms of corporate social responsibility. It's an area that has been under intense scrutiny in recent years due to rising concerns about climate change.
There are several actions organizations can take to be more environmentally responsible. For example, they can:
- Reduce pollution.
- Introduce recycling and waste initiatives.
- Increase their usage of renewable and sustainable energy.
- Offset their carbon footprint through green initiatives, such as rewilding or tree planting programs, or partnerships with environmental charities.
- Invest in green technologies.
Lego, for example, has set a goal to use only sustainable materials in the production of its famous toy bricks by 2030. It's achieving this by working with designers to replace plastic it has traditionally used with sustainably sourced polyethylene and plant-based materials. [1]
2. Ethical Responsibility
Ethical CSR initiatives include supplying benefits to an organization's stakeholders that go beyond legislative or mandatory duties. Ethical responsibility ensures that organizations act in a fair and ethical way toward the following groups:
- Employees and suppliers – by providing them with a safe working environment that is free from discrimination; ensuring fair pay; and delivering additional benefits, such as private healthcare, flexible working and extended maternity pay/benefits. Netflix, for example, offers new parents unlimited parental leave and staff can take unlimited vacation time. [2]
- Suppliers – by ensuring that supplier tender processes are run in a fair and transparent manner, and by partnering with suppliers that are also ethically, environmentally and socially responsible.
- Customers – by being transparent about terms and conditions, offering products or services that are safe to use and sustainable, and using a fair pricing system.
- Investors – by being fiscally prudent and transparent, and abiding by fiscal policies and regulations. Investors are increasingly choosing to put their money into socially and environmentally responsible projects, such as "green" organizations, or those that do not trade in tobacco or alcohol.
- Local communities – by using internal supply chains, products, services, or expertise in a way that benefits its local communities. For example, over 2,000 small, local businesses in the U.K. continued to deliver meals to local, low-income families during the pandemic, ensuring that many thousands of children were still provided with free meals while schools were closed. [3]
3. Philanthropic Responsibility
Philanthropic CSR initiatives are usually charity-based. They may include partnerships with charitable organizations or non-profits that align with the organization's own values and vision. Some organizations have even set up their own charitable trusts, while others invest in the community or participate in local projects.
Many organizations encourage and support employees to participate in volunteering activities for specific local charities, which they can do during their working hours. Others run matching gift programs, where workers' donations to charity are matched by the company.
Google is a prime example of a company that is actively engaged in corporate philanthropy. It runs multiple charity drives and has committed more than $100 million to global pandemic relief efforts – covering immediate relief activities to long-term recovery and future preparation initiatives. [4]
Tip:
Professor Archie Carroll's model of CSR, which is known as Carroll's Pyramid, suggests that organizations should look at four key areas when developing a CSR strategy – Economic, Legal, Ethical, and Philanthropic.
He suggests that organizations need to address each of these four areas to achieve a truly successfully and effective CSR strategy. To learn more, see our article, Carroll's Pyramid of CSR.
The Benefits of Corporate Social Responsibility
Some organizations are only spurred into developing a CSR program because they find themselves embroiled in a scandal. But most organizations have CSR programs that are embedded in their wider vision, mission and values.
And it's easy to see why. CSR programs can provide many benefits outside of reputational risk management. For example, they:
- Ensure companies are accountable, ethical and transparent. This can help to garner trust from investors, employees and customers.
- Give brands a competitive edge. Consumers are now extremely socially aware and perceptive, and are much more discerning about the brands they use. In fact, research has shown that consumers – and, in particular, Millennials – are willing to spend more on a product if it comes from a brand they believe is socially aware, suggesting that CSR has the power to not only do good, but to improve profits as well. [5]
- Improve the efficacy of charitable giving. CSR allows organizations to monitor how their charitable donations are being used, and ensure that charitable partnerships align appropriately with their business objectives.
- Improve talent acquisition and retention. CSR can positively impact employer branding, which in turn can help organizations to attract and retain talent. Research suggests that jobseekers are more likely to apply to, and stay with, organizations that are authentic, values-led and socially aware. [6]
- Enable community partnerships. Many companies use their CSR initiatives to work alongside, and give back to, the communities in which they operate.
- Drive funding and innovation. This is particularly the case in terms of greener technologies, with many companies investing in processes and raw materials that are environmentally friendly and sustainable. These investments are paving the way for new industry standards that could save companies significant amounts of money and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Can help organizations to win business. In some cases, organizations must demonstrate that they meet certain standards (above those which are legislated) in order to win business as a supplier or partner. Not only can this help to drive up organizational standards, but it can also improve market and even global quality standards, too.
How to Develop a Successful CSR Strategy
Here are five steps for creating a successful CSR strategy:
1. Do Your Research
Conduct polls and surveys to determine the causes that matter most to your key stakeholders – your investors, suppliers, employees and customers. A good CSR program needs buy-in from the bottom up, so it's vital that everyone's on board with the initiatives that you choose to go ahead with.
Think about your organization's core mission and values. What CSR initiatives would align well with them? For example, Ford Motor Co. has two key organizational objectives – to achieve outstanding fuel economy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Much of this is being achieved through its various CSR goals, which include achieving carbon neutrality for its vehicles by 2050, attaining zero emissions, and using 100 percent local, renewable energy by 2035. [7]
2. Audit Your Activities
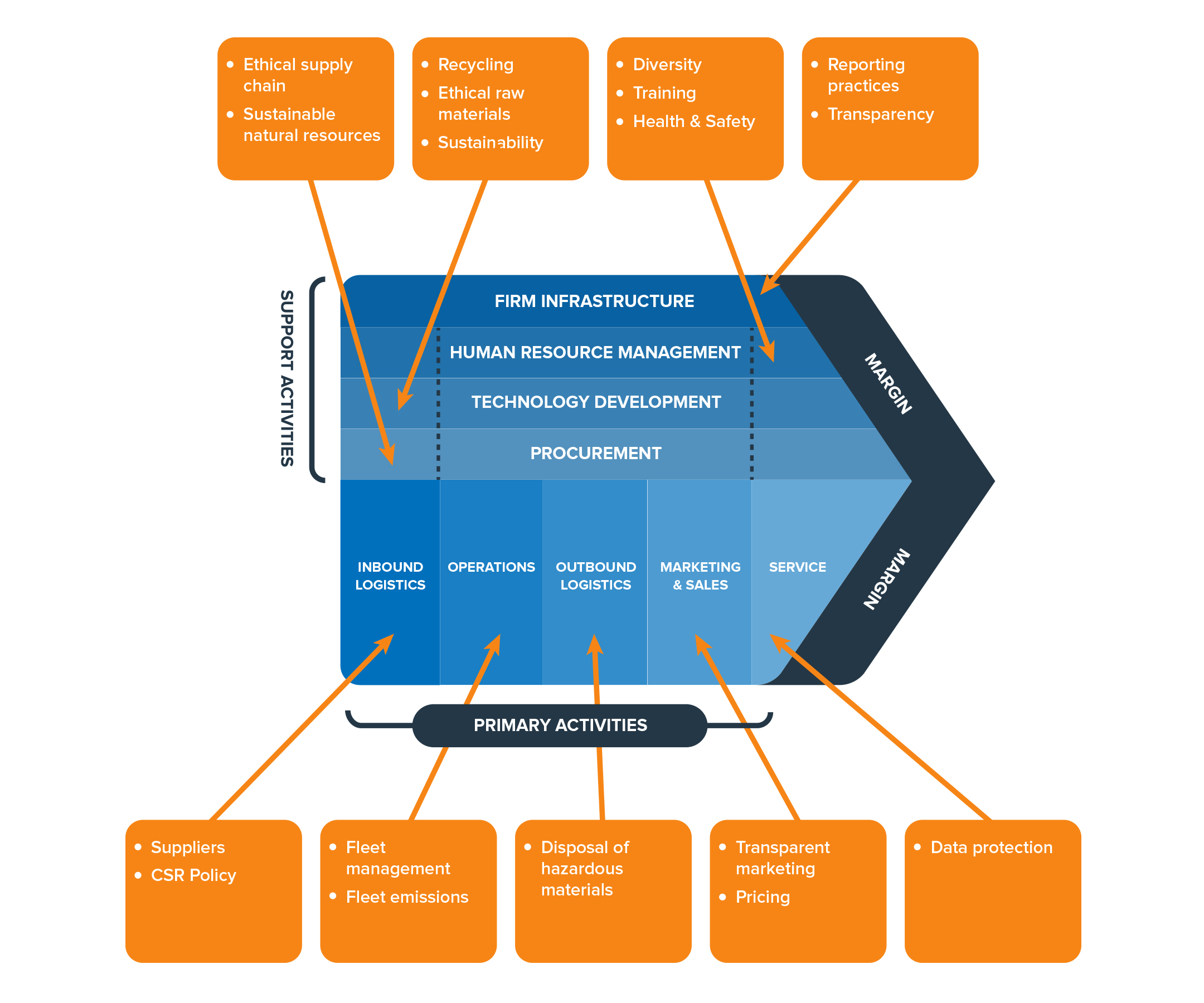
Make sure that you invest CSR funding where it will have the most impact in your organization. Value Chain Analysis is a great tool for doing this. It can identify the areas of your organization that are doing well, and ones that need improvement. While it's often used to improve business processes, you can also use it to audit your activities in each area of your business to check how socially responsible they are.
Start by listing all areas of your organization. Then write down which activities have a positive or negative impact. Finally, think about things you can do to improve your activities to make them more sustainable or responsible going forward.
Figure 1 (below) illustrates a Value Chain analysis that an organization might use to audit its activities and identify areas for improvement.
Figure 1: Using Value Chain Analysis to Identify Prospective CSR Initiatives
3. Set Specific CSR Goals
CSR is all about holding your organization accountable. Many companies set their goals with a focus on the triple bottom line – profit, people and planet.
Setting CSR goals relating to profit is relatively straightforward. But setting specific and achievable CSR goals relating to people and the planet can be tricky. Some common goals set around people include:
- The number of local jobs being created.
- The percentage of minority groups employed in the workplace and in leadership roles.
- Ensuring fair salaries regardless of age, gender or race, for example, by monitoring pay gaps.
- Reviewing talent acquisition and recruitment programs to attract a diverse pool of candidates.
- Benchmarking employee income and benefits against the living wage and industry standards.
- The percentage of employees receiving workplace training and education.
For organizations wishing to have a more positive environmental impact on the planet, common goals may include:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reducing carbon footprint.
- Investing in greener technologies.
- Improving recycling and waste management.
Tip:
Many organizations use the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), also known as the Global Goals, to guide their CSR goals. These represent a universal call to action to address some of the world's most pressing issues.
4. Measure Your Success and Report Back Regularly
Transparency is key when setting out your CSR strategy. This means that you need to follow through on the targets that you set for yourself by regularly monitoring and reviewing your progress toward them.
It's not enough to simply partner with a charity or write up a beautiful, glossy CSR report and hope for the best. You'll need to pin down the key metrics that will enable you to analyze your progress effectively. For example, if one of your targets is to have zero carbon emissions by 2050, then you'll need to put processes in place to monitor your emissions closely. This will allow you to build up an accurate picture of how well you're doing, and pinpoint what more needs to be done to ensure that you meet your target.
Make sure that your reporting is also clear and freely accessible to all. Some companies produce specific annual CSR reports, while others tie it in with their annual financial report. Not only does this ensure transparency and accountability, it also gives you a chance to celebrate your successes and show the world what your organization is doing to create a positive impact.
5. Listen and Adapt
The COVID pandemic has demonstrated just how vital it is for businesses to remain flexible and responsive to the needs of customers and employees. With many people's focus now firmly on health and safety, companies have adapted their supply chains and working practices to support employees and customers during the pandemic.
For example, the majority of large grocers introduced social distancing and mask-wearing policies even when though they were not mandated to do so by the law, while some manufacturers pivoted their activities to support the shortage of personal protective equipment (PPE) and hygiene products.
Many companies also adapted their working practices to protect the health and safety of workers by introducing flexible and virtual working arrangements, or enabling staff to go on furlough.
Similarly, the murder of George Floyd in June 2020 spurred many companies to take a stronger stance on racism by introducing zero-tolerance policies against discrimination, with several also partnering with anti-racist charities.
These kinds of initiatives demonstrate just how important it is for companies to be responsive to current events and trends. Customer demands often shift very quickly, so it's vital that your organization is attuned to these changing needs and can adapt its CSR strategy to support those needs, where possible.
Tip:
While most organizations deliver CSR strategies that align with their values and vision, some may use them to mask poor behavior. This is known as "greenwashing" and can often have a detrimental impact on reputation, if they are found out.
Be sure to develop CSR initiatives that are genuinely and authentically aligned to your values, vision and operational activities. For more on corporate ethics and responsibility, read our article, Jenning's Seven Signs of Ethical Collapse.
Key Points
Corporate social responsibility or CSR (also known as corporate citizenship and responsible business) refers to the activities undertaken by a company to create a positive social impact.
Generally, these activities fall into three key areas – environmental, ethical and philanthropic responsibility.
The vast majority of organizations develop CSR initiatives that align closely to their mission and values. But such programs can also offer additional organizational benefits, such as attracting and retaining talent, driving profits, and improving brand recognition and consumer loyalty.
You can create and deliver a successful CSR strategy by following these five key steps:
- Do your research.
- Audit your activities.
- Set specific CSR goals.
- Measure your success and report back regularly.
- Listen and adapt.
This site teaches you the skills you need for a happy and successful career; and this is just one of many tools and resources that you'll find here at Mind Tools. Subscribe to our free newsletter, or join the Mind Tools Club and really supercharge your career!




Comments (0)