PDCA (Plan Do Check Act)
Continually Improving, in a Methodical Way
Also known as PDSA, the "Deming Wheel," and "Shewhart Cycle"
Imagine that your customer satisfaction score on a business ratings website has dipped. When you look at recent comments, you see that your customers are complaining about late delivery, and that products are being damaged in transit.
So, you decide to run a small pilot project for a month, using a new supplier to deliver your products to a sample set of customers. And you're pleased to see that the feedback is positive. As a result, you decide to use the new supplier for all your orders in the future.
What you've just done is a single loop called the PDCA Cycle. This is an established tool for achieving continuous improvement in your business.
The PDCA approach was pioneered by Dr William Deming, and we've worked closely with The Deming Institute to produce this article. In it, we outline the key principles of PDCA, and explain when and how to put them into practice.
Click here to view a transcript of this video.
What Is PDCA?
In the 1950s, management consultant Dr William Edwards Deming developed a method of identifying why some products or processes don't work as hoped. His approach has since become a popular strategy tool, used by many different types of organizations. It allows them to formulate theories about what needs to change, and then test them in a "continuous feedback loop."
Note:
Deming himself used the concept of Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA). He found that the focus on Check is more about the implementation of a change.
He preferred to focus instead on studying the results of any innovations, and to keep looking back at the initial plan. He stressed that the search for new knowledge is always guided by a theory – so you should be as sure as you can that your theory is right! [1]
The Four Phases of the PDCA Cycle
With the PDCA cycle you can solve problems and implement solutions in a rigorous, methodical way. Let's look at each of the four stages in turn:
1. Plan
First, identify and understand your problem or opportunity. Perhaps the standard of a finished product isn't high enough, or an aspect of your marketing process should be getting better results.
Explore the information available in full. Generate and screen ideas, and develop a robust implementation plan.
Be sure to state your success criteria and make them as measurable as possible. You'll return to them later in the Check stage.
2. Do
Once you've identified a potential solution, test it safely with a small-scale pilot project. This will show whether your proposed changes achieve the desired outcome – with minimal disruption to the rest of your operation if they don't. For example, you could organize a trial within a department, in a limited geographical area, or with a particular demographic.
As you run the pilot project, gather data to show whether the change has worked or not. You'll use this in the next stage.
3. Check
Next, analyze your pilot project's results against the criteria that you defined in Step 1, to assess whether your idea was a success.
If it wasn't, return to Step 1. If it was, advance to Step 4.
You may decide to try out more changes, and repeat the Do and Check phases. But if your original plan definitely isn't working, you'll need to return to Step 1.
4. Act
This is where you implement your solution. But remember that PDCA/PDSA is a loop, not a process with a beginning and end. Your improved process or product becomes the new baseline, but you continue to look for ways to make it even better.
The four stages of the cycle are illustrated in Figure 1, below:
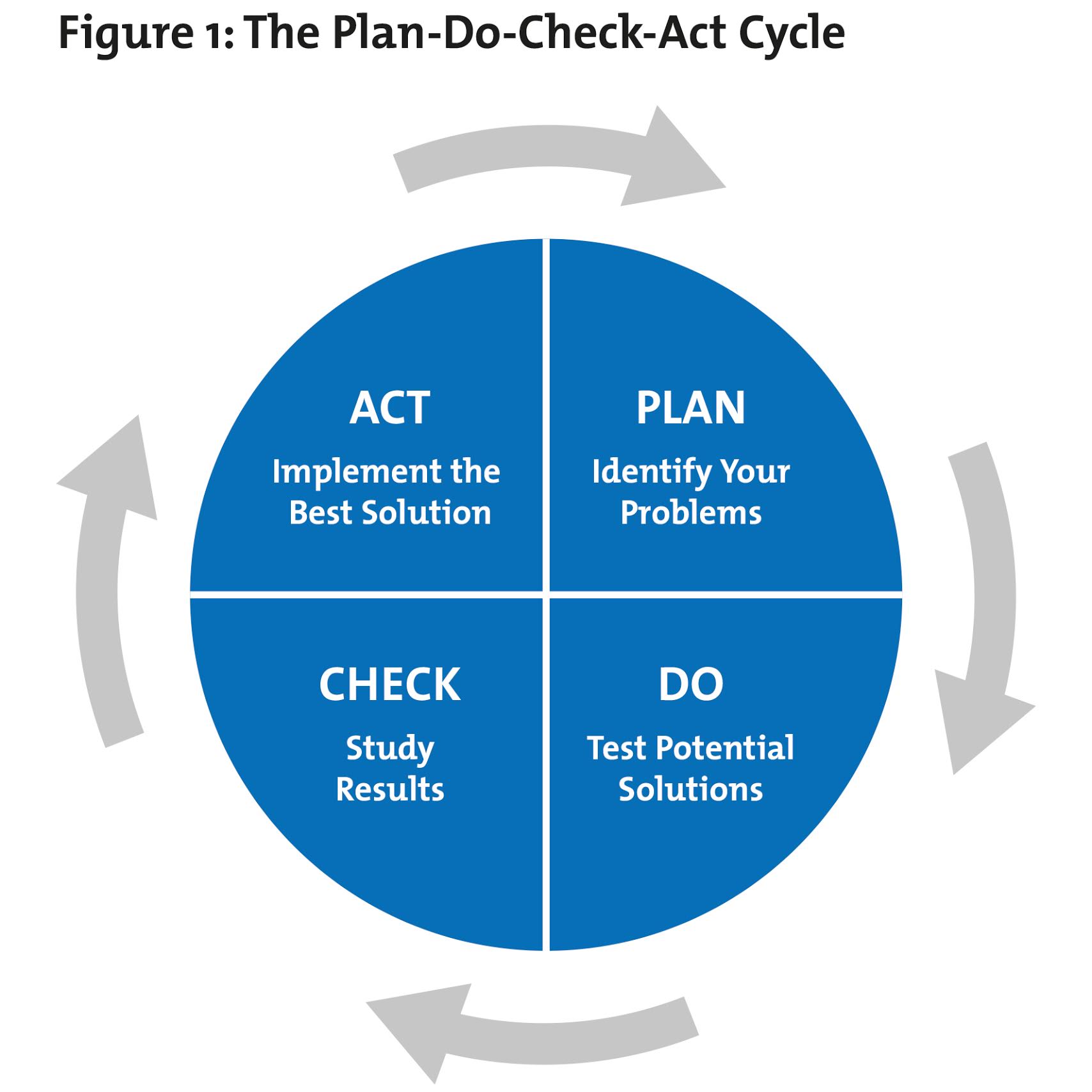
PDCA Model courtesy of The W. Edwards Deming Institute®.
When to Use PDCA
The PDCA/PDSA framework works well in all types of organizations. It can be used to improve any process or product, by breaking them down into smaller steps or development stages, and exploring ways to improve each one.
It's particularly helpful for implementing Total Quality Management or Six Sigma initiatives, and for improving business processes generally.
However, going through the PDCA/PDSA cycle can be much slower than a straightforward, "gung ho" implementation. So, it might not be the appropriate approach for dealing with an urgent problem.
It also requires significant buy-in from team members, and offers fewer opportunities for radical innovation – which may be what your organization needs instead.
How to Use PDCA to Improve Personal Performance
While PDCA/PDSA is an effective business tool, you can also use it to improve your own performance:
First, Plan: Identify what's holding you back personally, and how you want to progress. Look at the root causes of any issues, and set goals to overcome these obstacles.
Next, Do: When you've decided on your course of action, safely test different ways of getting the results that you want.
Then, Check: Review your progress regularly, adjust your behavior accordingly, and consider the consequences of your actions.
Finally, Act: Implement what's working, continually refine what isn't, and carry on the cycle of continuous improvement.
Key Points
The PDCA/PDSA cycle is a continuous loop of planning, doing, checking (or studying), and acting. It provides a simple and effective approach for solving problems and managing change. The model is useful for testing improvement measures on a small scale before updating procedures and working practices.
The approach begins with a Planning phase in which problems are clearly identified and understood, and a theory for improvement is defined. Potential solutions are tested on a small scale in the Do phase, and the outcome is then studied and Checked.
Go through the Do and Check stages as many times as necessary before the full, polished solution is implemented, in the Act phase of the cycle.
This site teaches you the skills you need for a happy and successful career; and this is just one of many tools and resources that you'll find here at Mind Tools. Subscribe to our free newsletter, or join the Mind Tools Club and really supercharge your career!




You're very welcome for the resource, and we're glad it was topical for you.
Don't forget that PDCA never really ends, although you would certainly implement at the end of the cycle if the solution fits the issue. PDCA would then be conducted on any other areas that have been impacted by the solution.
BillT
Mind Tools Team