Kano Model Analysis
Delivering Products That Will Delight

© GettyImages
AlexSava
Find the features that will make your customers rejoice.
Imagine the scene: your innovation team is excited about next year's product upgrades. The ideas have been flowing and your people have come up with lots of new features for your firm's best-selling product.
But, as project leader, you have some doubts. The cost of all the extra features will be considerable, and it will be very tough to deliver the finished product on budget and on time.
This is where a tool like the Kano Model can be useful. It's a simple and versatile technique for deciding which features a product or service should have, based on how much they will satisfy the customer.
In this article, we look at the origins and details of the Kano Model, and explore a five-step guide for using it to help you develop a product or service that will delight your customers – without bankrupting your business!
What Is Kano Model Analysis?
The Kano Model is a way of assessing the impact of services or product features on customer satisfaction. The model says that a product or service is about much more than just functionality – it's also about customers' emotions. For example, all customers who buy a new car expect it to stop when they hit the brakes, but many will be delighted by its voice-activated parking-assist system.
Adding one particularly attractive feature like this could delight customers and increase sales without costing significantly more. On the other hand, constantly introducing new features to a product can be expensive and may just add to its complexity without boosting customer satisfaction.
The model, therefore, encourages you to think about how your products relate to your customers' needs, while moving from a "more is always better" approach to product development to a "less is more" approach.
The Kano Model of product development and customer satisfaction was published in 1984 by Dr Noriaki Kano, Professor of Quality Management at the Tokyo University of Science. [1]
What Are the Elements of the Kano Model?
The model assigns three types of attributes (or properties) to products and services: Threshold Attributes, Performance Attributes, and Excitement Attributes. By assigning a product or service to an attribute, you'll be able to determine its impact on customer satisfaction. Let's look at each in more detail:
1. Threshold Attributes (Basics). These are the basic features that customers expect a product or service to have.
For example, when you book into a hotel, you'd expect hot water and a bed with clean linen as an absolute minimum.
2. Performance Attributes (Satisfiers). These elements are not absolutely necessary, but they increase a customer's enjoyment of the product or service.
Returning to our example, you'd be pleased to discover that your hotel room had free superfast broadband and a 4K TV, when you'd normally expect to find paid-for Wi-Fi and a standard TV.
3. Excitement Attributes (Delighters). These are the surprise elements that can really boost your product's competitive edge. They're the features that customers don't even know they want, but are delighted with when they find them.
In your hotel, that might be finding that the staff remember your name, or being offered a free meal or given a box of chocolates.
Figure 1, below, illustrates how the presence (or absence) of each of the three attributes in a product or service can affect customer satisfaction.
Figure 1 – The Kano Model
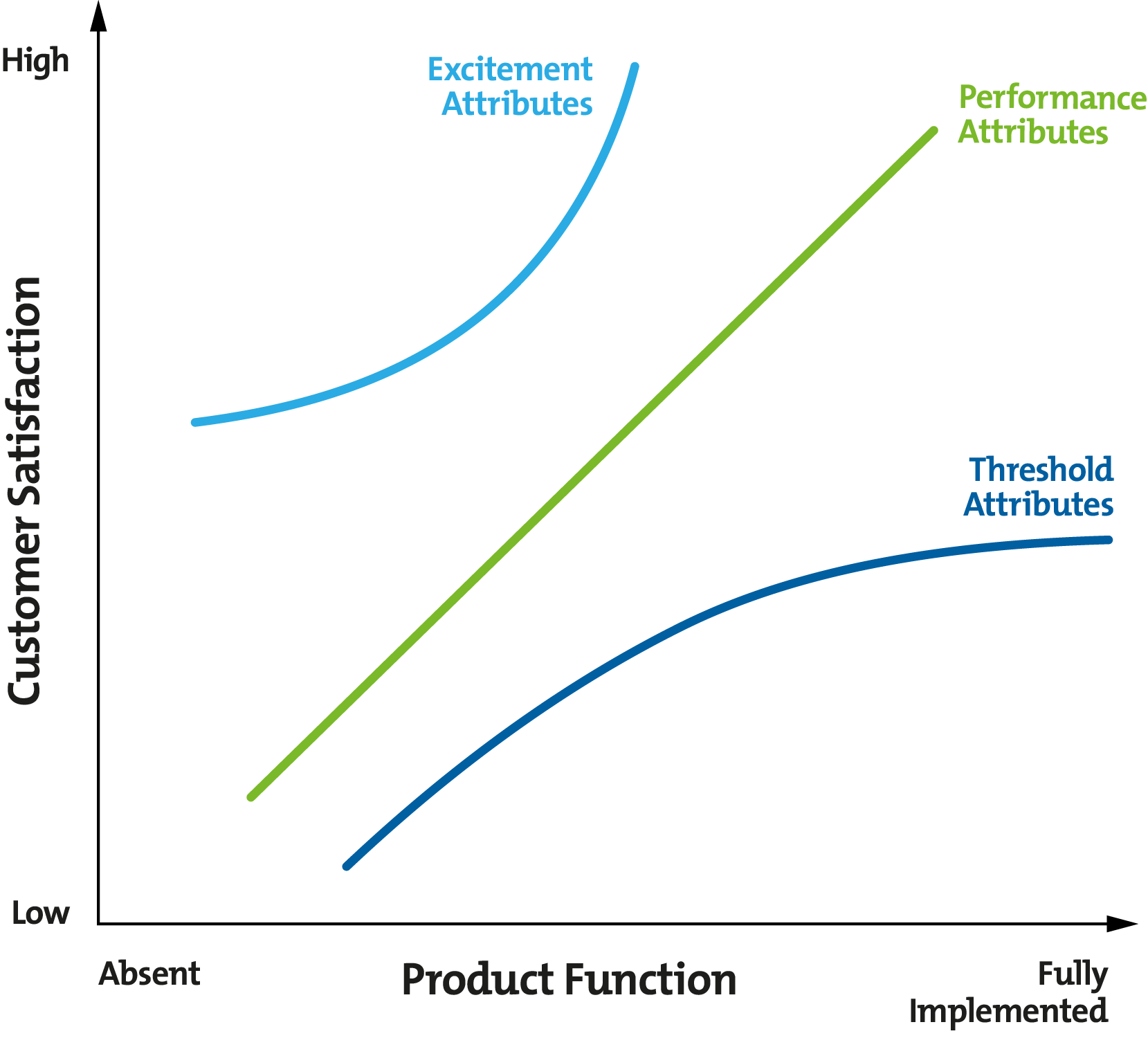
Diagram reproduced with permission from the Japanese Society for Quality Control. Original reference: Noriaki KANO, Nobuhiko SERAKU, Fumio TAKAHASHI, and Shin-ichi TSUJI (1984). 'Attractive Quality and Must-Be Quality,' Journal of the Japanese Society for Quality Control, Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 147-156.
You can see that, if a product's features don't meet a customer's Threshold Attributes, their satisfaction levels will be very low. However, even if you fully deliver on these, you won't impress customers that much.
Most products compete on Performance Attributes, where a customer weighs up one product against another and judges satisfaction by the availability of various features.
But they may discover an Excitement Attribute that really appeals, and gives them high satisfaction, even if it isn't perfectly implemented.
Figure 2, below, shows how customers' reactions to certain features (or the lack of them) can also have a negative or zero effect on satisfaction levels.
Figure 2 – A Development of the Kano Model
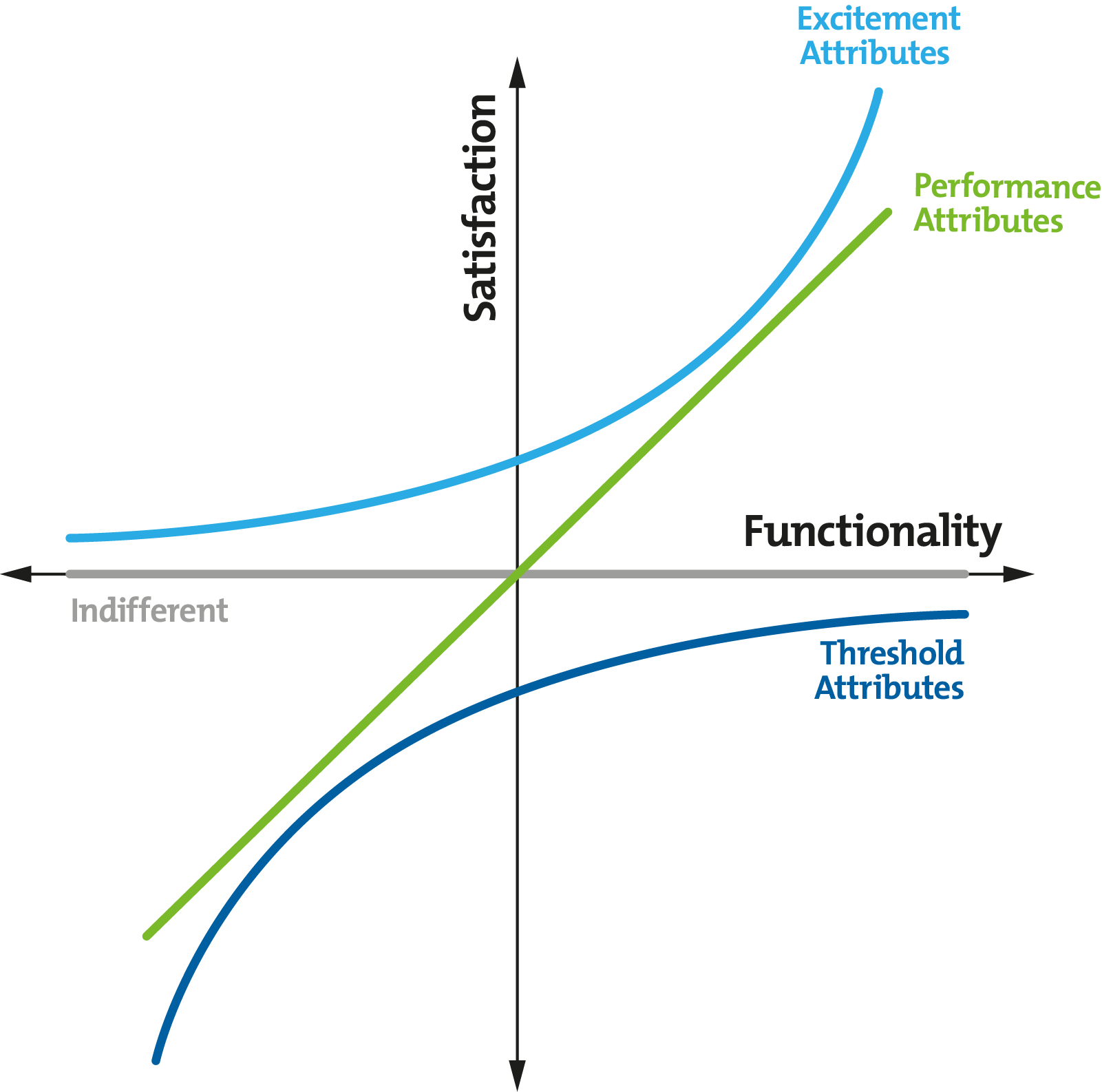
In the bottom-right quadrant, you can see that a product with just Threshold Attributes, even if it has a number of them, may not even lead to an indifferent level of customer satisfaction. (Indifference here is the baseline, shown along the x-axis.)
Customers begin to find your product attractive when you offer Performance Attributes, and it's along this line, in the top-right quadrant, that most organizations position their products in the market.
Excitement Attributes are the "wow factor" features that can give you a competitive advantage. These features can represent a good return on investment, because you don't need many of them to generate high levels of customer satisfaction.
Note:
It's important to consider the nature of your business, and the pace of change in your industry: today's Excitement Attribute can very quickly become tomorrow's Threshold Attribute!
For example, touch-screen technology in smartphones and tablets was an Excitement Attribute when it was introduced by Apple in 2007, but it soon became a Threshold Attribute common to many electronic devices.
How to Use the Kano Model
Before you apply Kano Model Analysis, be sure to find out what your customers really value. Never assume that you know! Ask them what they like, what they love, and what they dislike.
Our article on market research can help you with this process. Approaching your customers directly, using surveys or focus groups, for example, is also useful for keeping track of their changing expectations. And using Garvin's 8 Dimensions of Quality will help you to identify which qualities in particular are important to your customers.
Similarly, creating a customer journey map will give you a clear picture of customer touchpoints, and will provide insight into the experience from a customer's perspective.
Tip:
Make sure that, when you choose customers to give you feedback, you pick those who are typical of the market that you want to sell in.
Then, follow these five steps:
- Research and brainstorm all of the possible features and attributes of your product or service, and everything you can do to please your customers.
- Classify these as Threshold, Performance or Excitement Attributes, and add a fourth type, Not Relevant. These are the things that don't add value because customers don't care about them.
- Make sure that your product or service has all of the essential Threshold Attributes. If necessary, eliminate some Performance Attributes so that you can include these features.
- Assess the Excitement Attributes, and think about how you can incorporate some of them into your product or service. Again, if necessary, cut some Performance Attributes, so that you can afford to invest in your Excitement Attributes.
- Choose the Performance Attributes that you can deliver at a competitive price, while still maintaining an acceptable profit margin.
Tip:
Involve your customers in each of the five steps above. That way, you get their insights all the way through the process.
Key Points
The Kano Model of product development and customer satisfaction was published in Japan in 1984 by Noriaki Kano, Tokyo University of Science's Professor of Quality Management.
The model assigns three attributes to products and services:
- Threshold Attributes. These are the basics that customers expect.
- Performance Attributes. These increase a customer's enjoyment but aren't essential. Some of these may need to be scaled back, so that you can deliver Threshold and Excitement Attributes.
- Excitement Attributes. These are the surprise elements of a product or service that delight customers.
Understanding your customers' experiences and expectations, and effectively generating innovative ideas for improving your product or service, are key to carrying out Kano Model Analysis successfully.
This site teaches you the skills you need for a happy and successful career; and this is just one of many tools and resources that you'll find here at Mind Tools. Subscribe to our free newsletter, or join the Mind Tools Club and really supercharge your career!






Customers may be paying for satisfiers, but what creates a loyal customer are the features and services that customers have neither asked for or know that they need. Marketing research into customer loyalty demonstrates that customers quickly become adapted to the satisfiers and begin looking for more features, benefits and services. Companies that continually delight their customers develop a very loyal customer base. Think about Apple's fiercely loyal customer base. Intense customer loyalty is a source of competitive advantage and increases market share. The Net Promoter Score (NPS) developed by Reichheld is a measure of customer loyalty widely used by many companies.
Michele
Mind Tools Team
Thank you so much for updating this article. I know it will be an amazing resource.